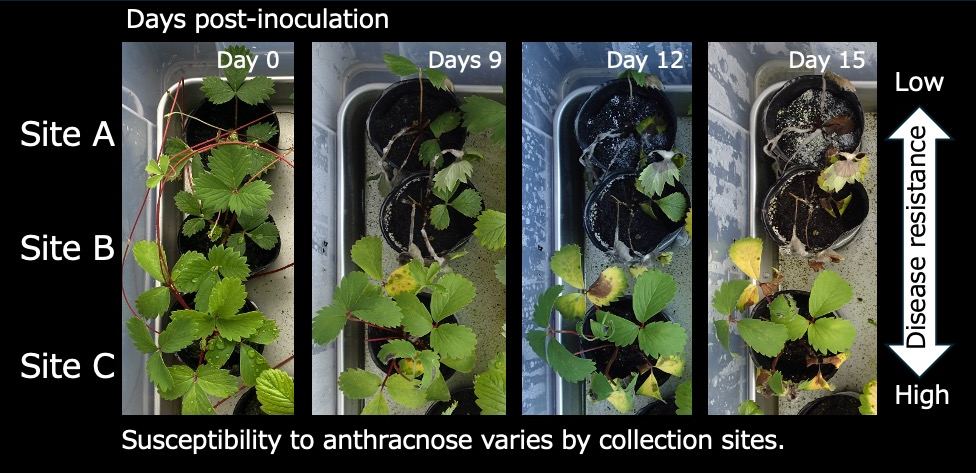
Contributing to the Development of Strawberry Varieties Resistant to Anthracnose

Anthracnose is a type of plant pathogenic fungus that can lead to wilting and plant death upon infection. In Japan, the annual economic impact of anthracnose on strawberry production is estimated to be around 3.5 billion yen1, making it one of the significant challenges for growers. Wild strawberries, with their high genetic diversity, are expected to exhibit greater resistance to diseases compared to cultivated varieties. This project aims to investigate the genes that show significant expression changes in wild strawberries infected with anthracnose, ultimately leading to the development of molecular markers for anthracnose resistance genes.
Overview of the Anthracnose Infection Experiment
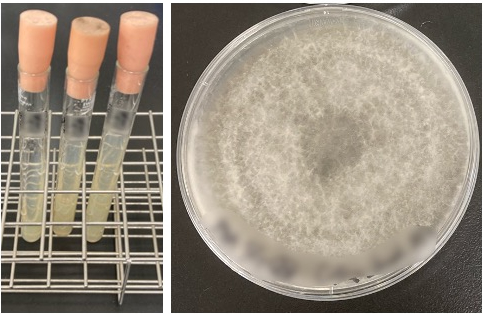
Anthracnose pathogens (Colletotrichum spp.) 2are cultured in the laboratory, and the collected fungal biomass is sprayed onto leaves to induce infection. Wild strawberry species and strains exhibiting strong resistance to infection are then analyzed for gene expression to identify key genes associated with anthracnose resistance.