Ultrasensitive Analysis of Functional Components in Wild Strawberries Using Ion Mobility MS

Strawberries contain functional components such as ascorbic acid, anthocyanins, and polyphenols like ellagic acid, which have been widely reported for their disease prevention and therapeutic effects. Developing strawberry varieties with high antioxidant activity can significantly enhance their market value. We focus on the functional components in wild strawberries, aiming to contribute to the development of strawberries with enhanced health benefits.
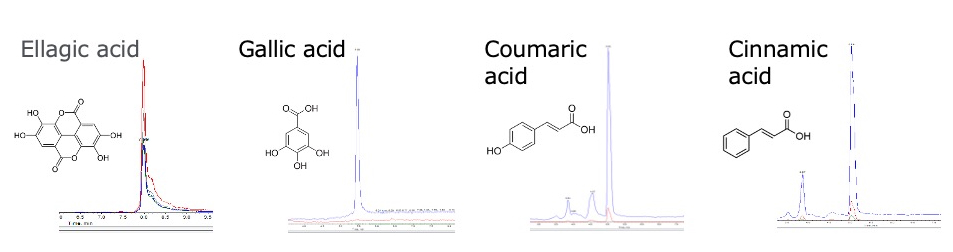
Analysis using ion mobility liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) shows that wild strawberries contain various functional compounds.
Wild strawberries are finely ground and subjected to ultrasonic treatment in a mixed solvent of acetone and water, followed by a 24-hour incubation. The samples are then analyzed using LC-ESI-IMS-MS/MS. Ion mobility analysis not only enables the detection of these functional components in wild strawberries but also allows for their precise quantification.
Detection of plant hormones in strawberries

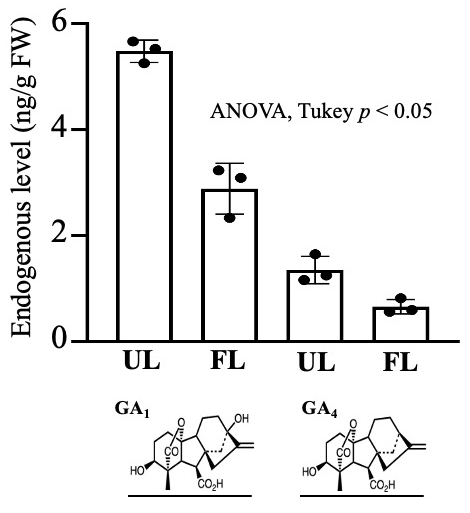
Analyze plant hormones in various strawberry tissues at different growth and physiological stages to collect data that supports the optimization of cultivation techniques and quality improvement. Our group specializes in the detection and quantification of plant hormones, particularly brassinosteroids, which are typically challenging to analyze.
Figure on the left: Detection of gibberellins, a type of plant hormone: comparison of endogenous gibberellins (GA) in unexpanded leaves (UL) and fully expanded leaves (FL) of Fragaria vesca.
